Cyber Security News Aggregator
.Cyber Tzar
provide acyber security risk management
platform; including automated penetration tests and risk assesments culminating in a "cyber risk score" out of 1,000, just like a credit score.Revealed: The Most Popular Hacking Tools on the Dark Web
published on 2022-06-08 13:00:58 UTC by Yuval ShibiContent:
Hacking has long been a global pandemic. It is estimated that over 30,000 companies suffer a cyberattack, daily. On the dark web, we are able to find the tools and kits used by hackers to conduct these attacks to compromise companies, individuals and brands for their personal gain.
Where can hacking tools be found on the deep and dark web?
We can often find hacking tools on:
- Hacking forums – in which cybercriminals post, discuss and trade them
- Marketplaces – where vendors list them for sale alongside a short description to attract potential buyers
- Chat applications – such as Telegram, where both threat actors and cybercriminals discuss and post hacking tools.
What are the differences between certain hacking tools and others?
Today we’d like to split cyberattacks into two categories, using two parameters: how often and widely they are mentioned on the web, which affects its popularity, as well as the levels of access they provide to the target system, which can determine how much damage they can cause. For example, an SQL injection vulnerability may only enable them to steal data from the vulnerable database, whereas a successful phishing attack may result in compromised credentials or the installation of malware on a compromised system.
The most popular hacking tools on the deep and dark web
There are many hacking tools on the web but in this review, we will discuss some of the most widely common tools out there: Malwares, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), Ransomwares, Phishing, and DDoS attacks.
So let’s start.
Malwares
Malware (short for “malicious software”) refers to software (such as viruses, trojans, and other destructive programs) used by attackers and threat actors to infect systems and networks. These computer programs are designed to interfere with a computer to carry out virtually any action an cybercriminal desires – exploring, stealing or conducting any behavior on the network of their target.
What’s the risk? Theft of sensitive data such as financial details, credentials, sensitive corporate information or PII.
Where can you find malware tools on the web? On dark web hacking forums, datastores (marketplaces), and chat applications.
How accessible are malwares? These tools are typically offered for sale for hundreds of dollars on dark web hacking forums.
A few examples of mentions of malwares on the dark web:
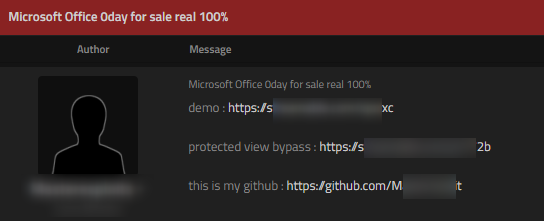
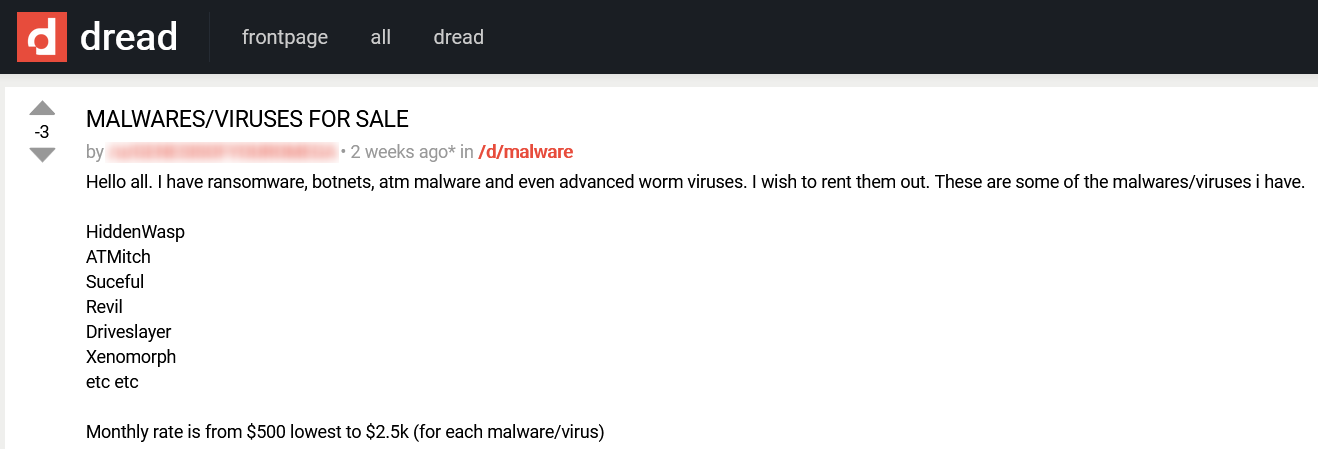
RATs – Remote Access Trojans
RAT is a type of malware that enables hackers to remotely control a computer that was already infected with the malware. After the RAT is installed on a compromised system, the attacker can send commands to it and receive stolen data in response. The RATs can be attached to emails, hosted on a malicious website, or exploit a vulnerability in an unpatched machine. RATs pose a high risk because they provide the attacker with a high level of access control over a compromised system because they provide the same level of functionality as legitimate remote system administration tools.
What’s the risk? The hacker can achieve almost any objective on the infected system, including downloading and deploying additional functionalities necessary to achieve their goals.
Where can you find RATs trading on the web? RATs are usually discussed on dark web hacking forums and on chat applications such as Telegram.
How accessible are RATs? RATs can often be bought at a low price, and sometimes for free, making them extremely accessible for any cybercriminal who is looking to gain access to a remote system.
An example of a post listing RAT features:
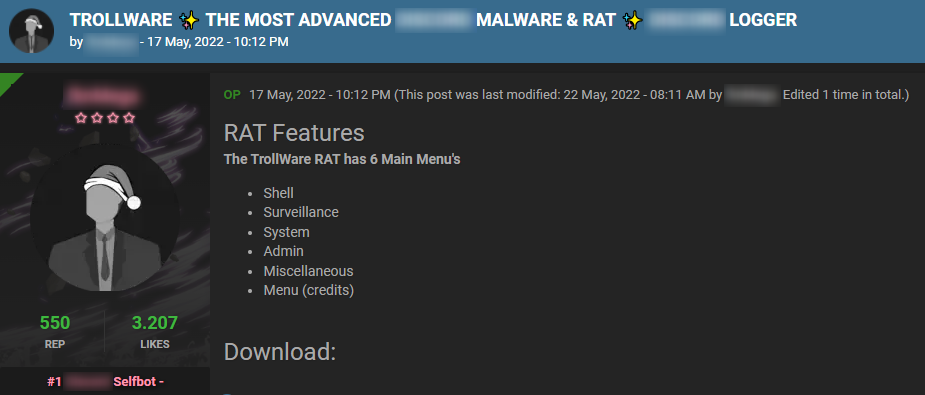
Ransomwares
Ransomware is a malware designed to prevent users or organizations from accessing files on their computers. By encrypting files and demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key, hackers force organizations to pay ransoms in order to unlock their files and data. Various ransomware variants have added additional features, such as data theft, to provide victims with a further motivation to pay the ransom.
What’s the risk? Data theft and leakage, money loss, and other vulnerabilities that were created following the leak of the data.
Where can you find ransomware trade on the web? Ransomwares are usually traded on dark web hacking forums, marketplaces, paste sites and chat applications.
How accessible are ransomwares? Ransomwares tend to be more expensive than different vulnerabilities offered for sale. They can cost hundreds and thousands of dollars. However, their popularity among threat actors and cybercriminals makes them accessible and very easy to find on the dark web.
A few examples of posts featuring ransomware:
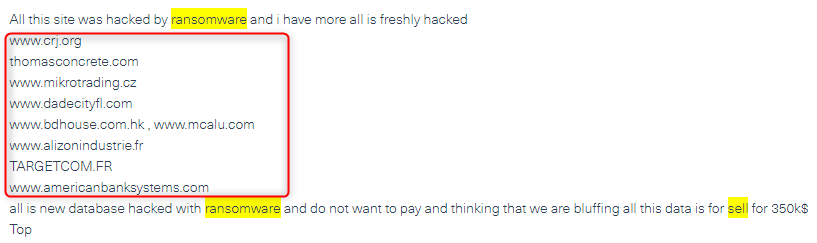
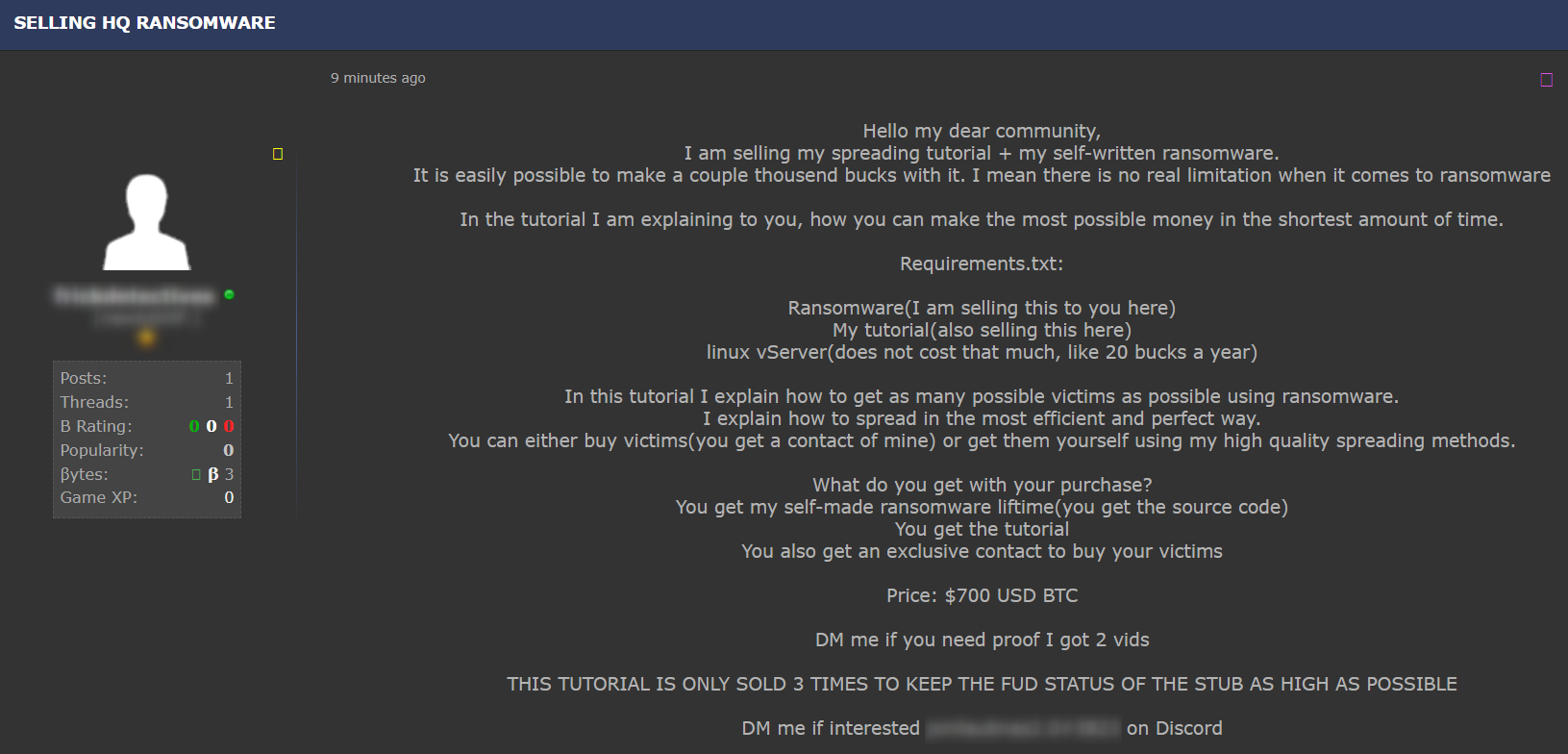
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cybersecurity attack in which malicious actors pretend to be someone they are not. Phishing is a type of social engineering, which is a generic term used to describe attempts to manipulate or trick computer users. The hacker’s method in this case is accessing the target from the least expected and suspicious platforms – any platform the targeted victim, usually an employee, uses – including social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Instagram, email service providers, etc.
What’s the risk? influencing a user to install malicious files, click on malicious links, or share sensitive information such as credentials, scripts, PII, credit card information, etc.
Where can you find phishing tools on the web? Many phishing tools can be found on Hacking forums, and chat applications such as Telegram and dark web marketplaces.
How publicly accessible is it? Can be shared for free or sold for less than $10.
An example of phising pages for sale:
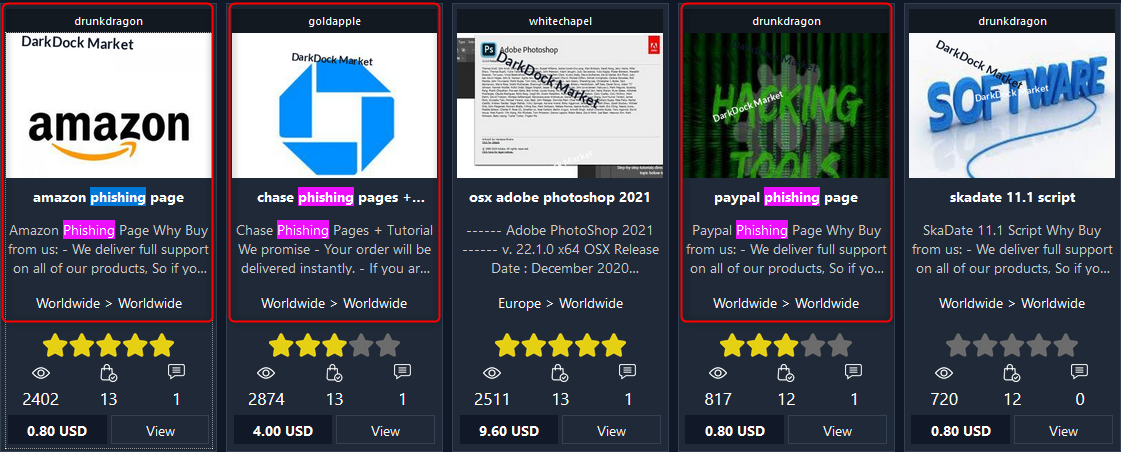
DDoS Attacks
A DDoS attack works in the same way as an unexpected traffic jam preventing regular traffic from reaching its destination. DDoS attacks are malicious attempts to disrupt normal traffic on a server, service, or network by flooding the target with internet traffic. The effectiveness of DDoS attacks is achieved by using a large number of compromised computers. When a victim’s server or network is targeted by a botnet, the botnets send requests to a victim’s IP address in order to overload the server or network, and by that causing a denial-of-service to normal traffic, which blocks the flow of information across the network.
What’s the risk? This attack blocks the access to the site.
Where can you find DDoS services and tools on the web? DDoS services and tools are offered for sale on dark web hacking forums, marketplaces and chat applications.
How accessible are DDoS tools? DDoS services and tools are posted on the dark web either for free or for low prices ranging from $5 to $20.
An example of a post featuring a DDoS script:
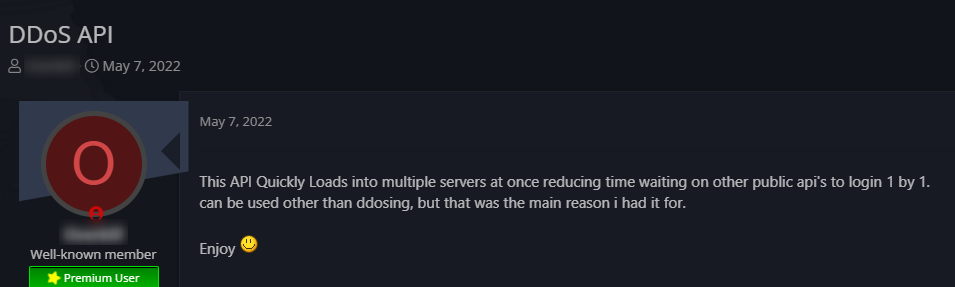
As you can see, finding hacking tools and vulnerabilities is easy and can be quickly found on the dark and deep web. Many of these tools and services are free and cheap which means hackers can gain access to login details and PII with very little cost. This means that cyberattacks are no longer limited to so-called “professional hackers”.
With the plethora of cyberattack guides, tutorials, and scripts available on the dark web, anyone who has the will and time to enter the dark web can acquire the tools needed to launch a cyber attack. This is why the deep and dark web have become the frontier that every company needs to guard to protect its brand, reputation, data and employees.
https://webz.io/dwp/revealed-the-most-popular-hacking-tools-on-the-dark-web/
Published: 2022 06 08 13:00:58
Received: 2022 06 08 13:10:31
Feed: Webz.io Dark Web Posts Dark Web News
Source: Webz.io Dark Web Posts
Category: News
Topic: Dark Web
Views: 15
