Cyber Security News Aggregator
.Cyber Tzar
provide acyber security risk management
platform; including automated penetration tests and risk assesments culminating in a "cyber risk score" out of 1,000, just like a credit score.The Top Ways Hackers Steal Passwords and Post Them on the Dark Web
published on 2022-11-02 10:40:54 UTC by Yuval ShibiContent:
Over the past years, we have seen an increasing number of stolen credentials across the deep and dark web. This trend is not going to change in the foreseeable future since cybercriminals and hackers are constantly looking for new ways to crack passwords in order to bypass security controls and hack into systems and databases.
When an attacker gains access to your password, they can steal your identity, money, and sensitive information, gain access to related accounts, install malware, conduct fraudulent activities, espionage, and sabotage, or sell your credential to unscrupulous buyers.
The type of attacks can be broadly classified into two major categories:
- Targeted attacks – The attacker would launch the attack only against a specific target.
- “Shoot gun” attacks – The attacker conducts the attacks on a wide range of targets by using a “shoot wide and hit anything” approach.
What are the top techniques hackers use to steal passwords?
Malware
Malware is a common tool criminals use to steal credentials. In the world of computer malware, you can find a broad range of threats that do everything from secretly tracking your movements to outright locking up your system and destroying your files.
Some top examples of malware types:
- Keylogging malware tracks the keystrokes typed directly onto a keyboard.
- RedLine stealer malware takes advantage of your browser’s mission to make online life easier by stealing almost any kind of valuable information on the computer, such as browser-saved passwords, executing commands on the computer, and downloading and installing other programs onto the infected machine.
- Spying malware can hack into webcams to watch and record you.
- Ransomware is malware designed to deny a user or organization access to their computer files by encrypting these files and demanding ransom for the decryption key.
Malware is a planned cyber attack that is usually aimed at specific targets, including large groups or whole companies.
Example of stolen credentials obtained with “Redline” stealer malware
The following post is taken from dark web marketplace Russian market, which offers login credentials for sale. On the right side of the screenshot, it states that the stolen credentials are obtained by the stealer Redline malware.

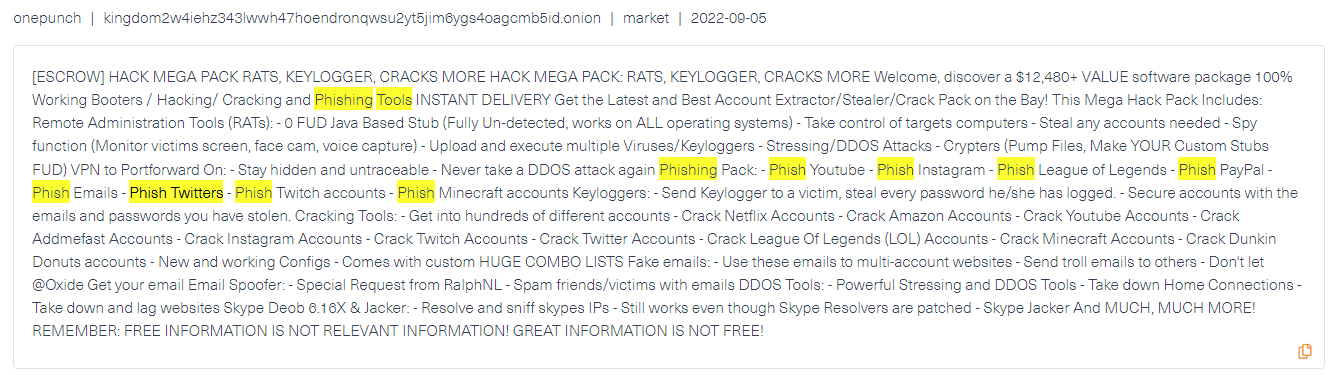
Phishing
Nowadays, it’s hard to tell spam from legitimate emails, documents, or links. Take our email inbox, for example, some of the spam emails might be phishing attempts, but the real problem is phishing has become sophisticated and widespread. Spam and phishing are both social engineering techniques that use advertisements and junk emails to sell products or for marketing. However, in the case of phishing, it is regarded as a form of cyberattack since cybercriminals use phishing emails to steal passwords, credit card details, and any other type of PII. Due to the fact that it doesn’t require high technical knowledge, phishing is one of the most preferred forms of cyberattacks among hackers. Instead of creating a malware code, all the hacker needs to do is trick the user into revealing their credentials and disclosing them.
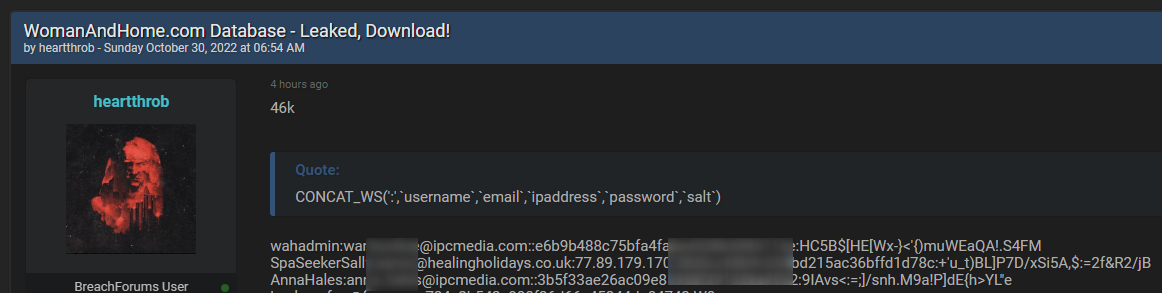
Data breaches
Millions of accounts are hacked on a daily basis by testing all possible combinations of usernames and passwords taken from stolen databases. This is an example of “Shoot gun” attacks, in which hackers use leaked data to hack various platforms. Then they dump the database, steal the account information, and use them for their own use or sell it on the dark web.
Since many people use the same password on different sites this form of attack poses a high risk since the attacker can compromise millions of accounts in a single attack, including their business accounts to access their organization’s system.
How to monitor compromised passwords on the dark web?
In order to protect against cyberattacks, it’s important to monitor leaked passwords across the deep and dark web. Finding stolen credentials as soon as they are published is one of the key ways to provide alerts in time to take action and mitigate cyberattacks.
Webz.io works with some of the world’s leading cyber intelligence and event monitoring companies to provide them with structured and enriched deep and dark web data to help track compromised data that was posed after an attack launched by password-stealing techniques. By using Webz.io’s Cyber API and Data Breach Detection API, cyber intelligence companies can identify compromised data that can be used to gain unlawful access to their customers’ platforms.
https://webz.io/dwp/the-top-ways-hackers-steal-passwords-and-post-them-on-the-dark-web/
Published: 2022 11 02 10:40:54
Received: 2023 02 08 12:46:27
Feed: Webz.io Dark Web Posts Data Breach Threats
Source: Webz.io Dark Web Posts
Category: News
Topic: Data Breach Threats
Views: 17
