Cyber Security News Aggregator
.Cyber Tzar
provide acyber security risk management
platform; including automated penetration tests and risk assesments culminating in a "cyber risk score" out of 1,000, just like a credit score.The Top 10 Challenges to Accessing the Dark Web
published on 2022-08-10 11:43:18 UTC by Yuval ShibiContent:
Dark web content is considered to encompass about 96% of all the content found on the web. This means that only 4% of the entire web is indexed and can be accessed through a mainstream search engine. This means that a significant part of the dark web is less accessible and largely unknown for online users.
What is the deep and dark web?
The dark web is a part of the deep web accessible only through special tools and browsers, such as the Tor browser. In contrast to the deep web, which contains both legal and illegal content that’s just less accessible, the dark web is mainly anonymous and is more commonly used for illegal web activities.
The deep and dark web consist of platforms and sites that require special software or authorization to be able to access them. Dark web content can only be entered by using specific browsers or through specific network configurations. This makes the dark web, and more specifically, places like dark web marketplaces, carding and hacking forums, a fertile ground for illicit activities such as drug trafficking, financial fraud, and hacking.
How can you access the dark web?
TOR (The Onion Router) is considered the most popular dark web network used for accessing dark web content. Because TOR allows its users to remain anonymous by keeping users’ IPs hidden, it has attracted many threat actors whose prime concern is to remain active and safe from law enforcement. Dark web content is also designed to be less accessible to the general public, and more accessible to users who know what they’re looking for on the dark web, whether it be illicit or legal content – and know how to search for it. All of this makes accessibility a big concern, whether for individuals or law enforcement and cyber intelligence teams (read more on that later in this post).
But what are the main challenges to accessing the deep and dark web?
The top challenges to accessing deep and dark web content
The difficulty in accessing deep and dark web content has also affected organizations and enterprises. Because a lot of the content and dark web activities happen under the radar, there is a widespread abuse of brands and individuals. From trade of compromised company data to stolen PII, the dark web encompasses a lot of information that needs to be tracked. But there are a few obstacles in the way of accessing that important information.
Let’s take a look at the 10 challenges brands need to overcome to monitor the dark web:
Challenge #1: Unsearchable content
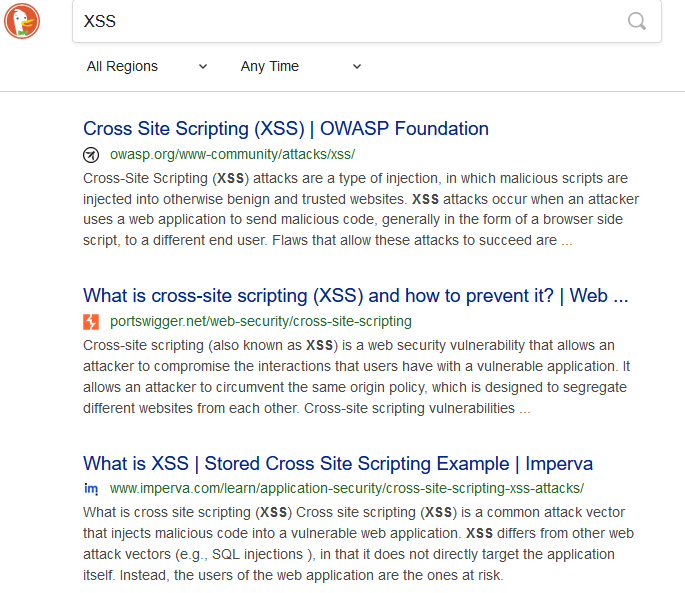
As mentioned before, deep and dark web sites are not indexed, which means they won’t appear in search results on popular search engines like Google. When searching for content, you’ll need to know the exact Onion URL of the site you’re looking for. Even the official search engine for TOR, DuckDuckGo, doesn’t index onion sites, so it won’t show sites whose admins opted to stay off the grid.
For example, below (see image) we ran a search on the term “XSS”, a well-known Russian hacking forum, on DuckDuckGo. The results listed several definitions and explanations of the XSS attack, but the actual site is not listed. This makes it harder to access the site if we don’t know the exact domain.
Challenge #2: Domain and Mirrors
Onion sites regularly change domains on the dark web in order to make it harder to track them, or when the site collapses. This can also happen to deep web sites. This results in multiple complete copies (domains) for a site, called mirrors. In case one mirror is temporarily unavailable, followers usually have more than one mirror to access the original site. This also raises the possibility of scam sites pretending to be the original, misleading users who will trust them to be the original sites. To prevent that, sites ask their users to check if the mirror they’re using is an official mirror.
For example, in the image below you can see that the dark web marketplace Kingdom Market is asking users to click on the mirror they are using from a list they provide to verify whether the URL they’re using is indeed an official and protected mirror.
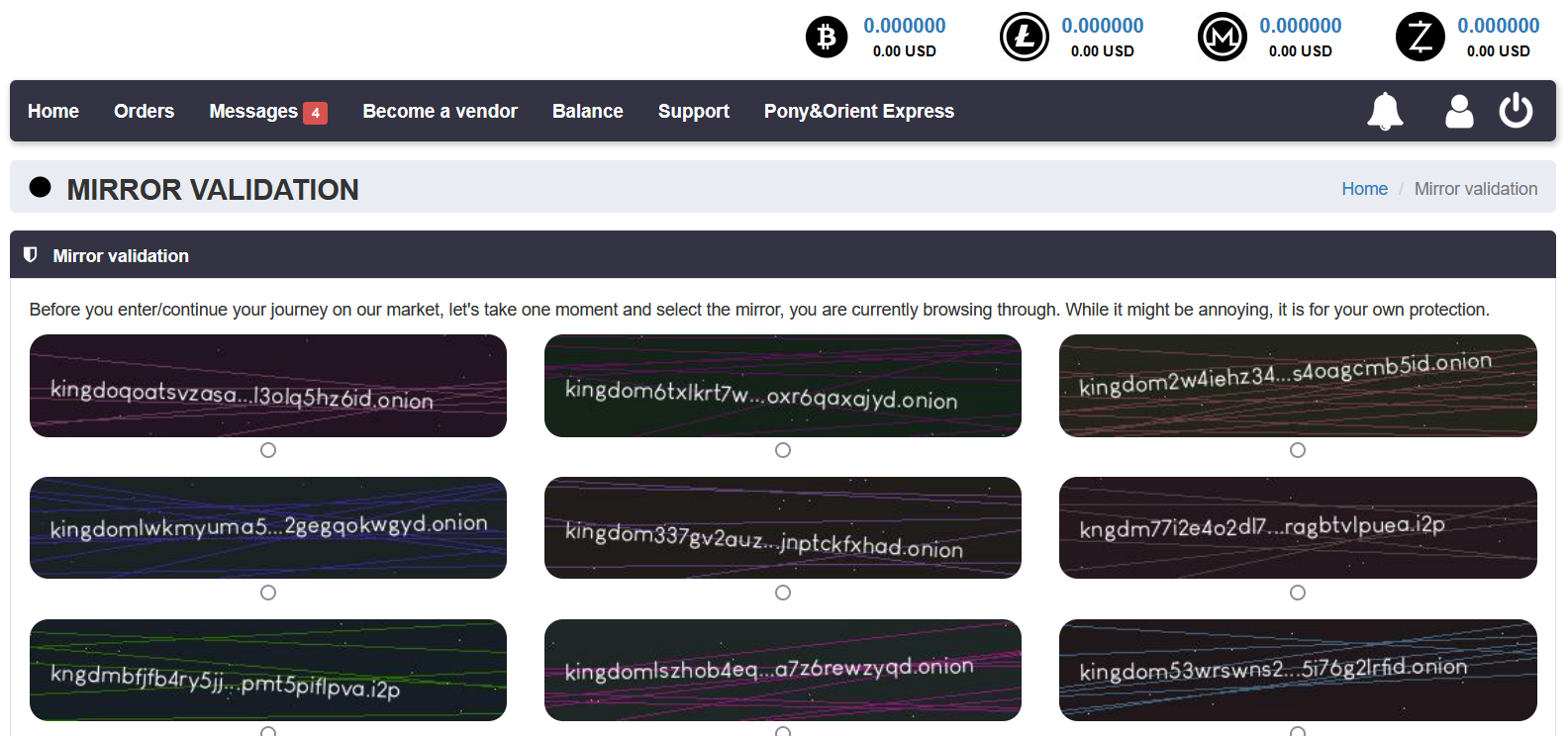
Challenge #3: Instability of sites
The unstable nature of Tor sites is ingrained in the fact that the admins aim to keep their content under the radar. This is even more true when it comes to admins of dark web sites that host illicit content. This means that onion dark web sites are increasingly difficult to track over a long period of time. In addition, many onion sites are regularly under construction, which leads to data loss and content changes. Sites are frequently shut down and are back up, many times because admins choose to shut them down in the first place to avoid being caught.
Another reason dark web sites are so elusive is because some of them are seized by law enforcement agencies, which we witness happening on a more frequent basis over the past years. A good example of one is the shutdown of the popular hacking forum Raidforums in April 2021.
Challenge #4: Reliability
Many TOR, deep and dark web platforms tend to be untrustworthy as they are operated and managed by cybercriminals. We see a lot of exit scams – for example, dark web marketplaces that stop shipping orders while still receiving payment for new orders. Some of the scams impact many because if the site has a good reputation, it could take some time before its users realize that orders are not shipping.
Below you can see an example of such a wide scam of Aurora Market which made an exit scam in April 2021, only a year after it was first established.

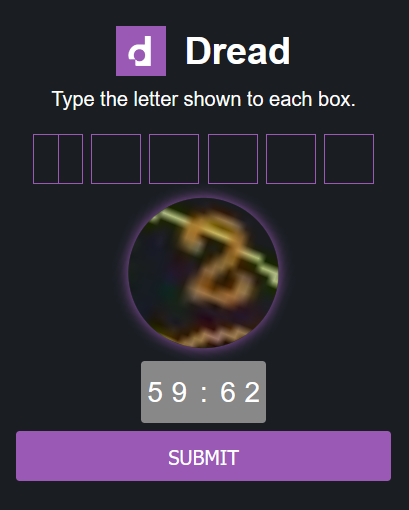
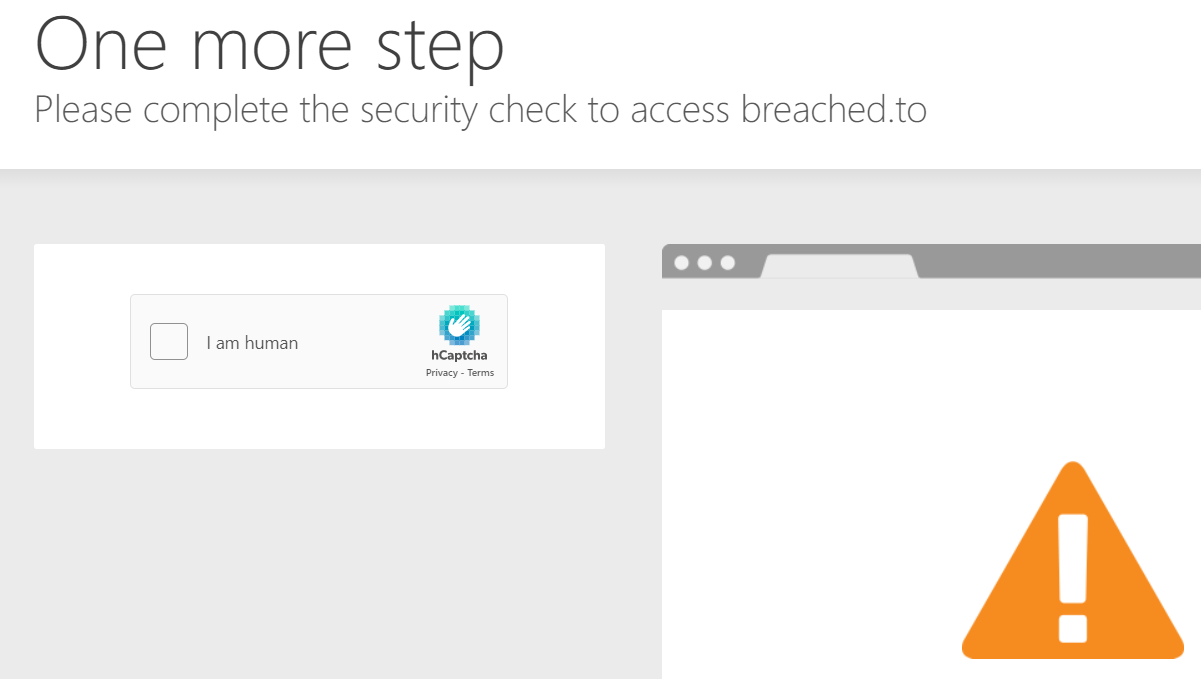
Challenge #5: Manual anti-bot verification and CAPTCHA tests
Anti-bot verifications are tools used to differentiate between real human users and automated users, such as bots. Once a bot is discovered, the site blocks its access and the dark web content becomes inaccessible.
Below are a few examples of different anti-bot tests. The same goes to CAPTCHAs, which stand for the Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, that provide challenges that are difficult for computers to perform but relatively easy for humans. This prevents automated spam activity and posts on the platforms.
Challenge #6: Cloudflare
Accessing deep web sites that are blocked with Cloudflare is considered as one of the biggest challenges in monitoring illicit content these days. Cloudflare is a secure content distribution network (CDN) that uses proxy servers to make sure that the access, content, and delivery of content is safe. To assure that it blocks the access to sites that use the service until the user proves she or he is human by solving a CAPTCHA. It also blocks IP addresses that are known for being sources of spam and malicious content by default. Cloudflare service is used on several deep web illicit sites such as BreachedForums, Nulled, Hackforums, and others.
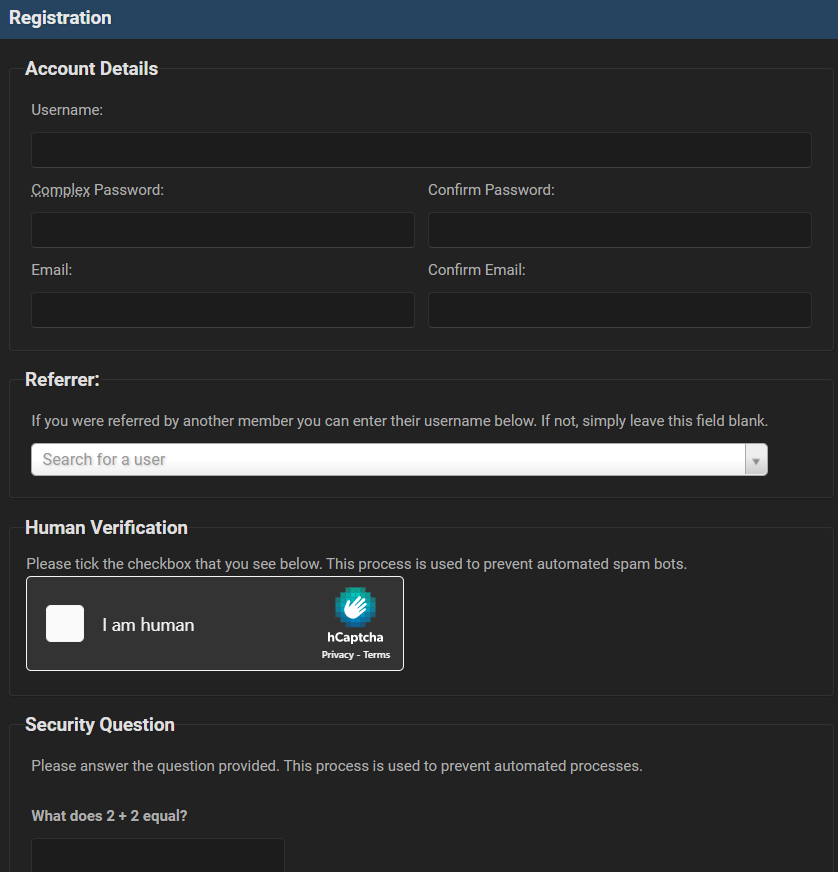
Challenge #7: Protected Login
Illegal platforms on the deep and dark web restrict access to them using different methods like admin approval, payment or even invitation-based access by another forum member using an invite code.
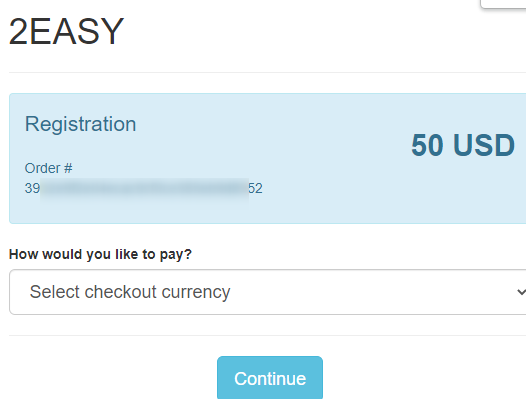
Challenge #8: Paywall
Just like they’re used on legitimate sites, paywalls are also used to prevent access to deep and dark web content without a paid subscription. Users are blocked by paywalls and required to pay fees in order to gain access to the site’s content.
For example, as you can see below, the dark web 2easy marketplace requires 50$ for first access.
Challenge #9: Paid invitation
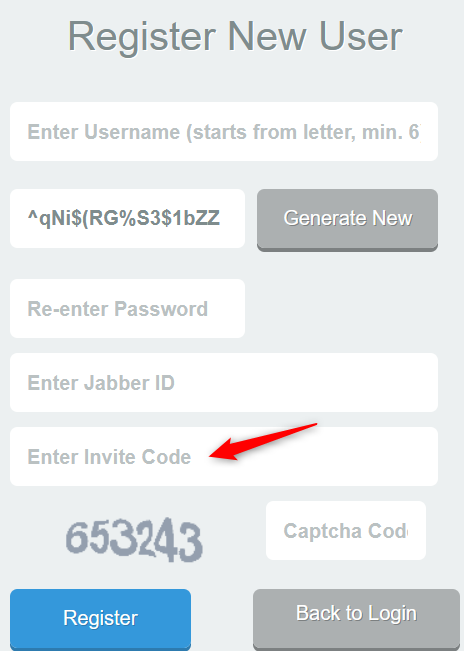
Some deep and dark web platforms require an invitation code which users can either buy on a marketplace or get from existing forum members.
Below is an example of a paid invitation in a registration page to a dark web credit card shop.
Challenge #10: Hidden Content
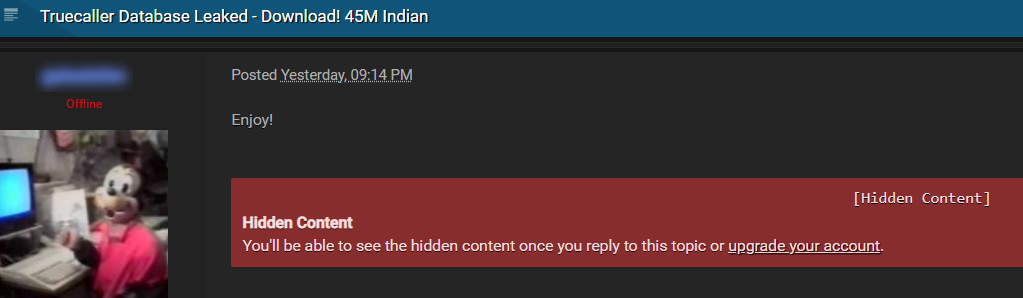
Although it may not make a lot of sense, accessing deep and dark web illicit sites does not mean you can view the entire content on it. Some platforms block their content to make users pay for it or commit other actions such as commenting or posting content themselves.
So how can companies access dark web content at scale?
The deep and dark web is a popular space for the cybercriminal community. It is the place where cybercriminals post leaked credentials, hackers share breached enterprise data, threat actors trade zero day vulnerabilities and exploits, and ransomware groups publish access to cracked software. For this reason, monitoring illicit content from TOR, the deep and dark web is crucial.
The only way to overcome these challenges and find these critical early indicators and threat intelligence on attacks against brands and individuals, is by using structured and enriched data from the deep and dark web.
Webz.io automatically crawls illicit deep and dark web content to provide near-real time data that helps the world’s largest enterprises stay ahead of the cybercriminal community.
https://webz.io/dwp/the-top-10-challenges-to-accessing-the-dark-web/
Published: 2022 08 10 11:43:18
Received: 2023 02 08 12:46:29
Feed: Webz.io Dark Web Posts Web Intelligence
Source: Webz.io Dark Web Posts
Category: News
Topic: Web Intelligence
Views: 19